Building an AI agent used to mean hiring engineers, stitching APIs together, and maintaining a messy stack of tools. In 2026, it can be much simpler. You create a role based assistant, teach it your content, then deploy it where people already interact with your brand.
This guide focuses on a practical, no code workflow using Agent.so. It is built around one idea: your agent should feel like a specialist, speak in your tone, and live in the channels that matter.
What an “AI Agent” Means Here
Here, an “AI agent” is a chat based assistant that behaves consistently like a specialist. You configure it with instructions and knowledge so it can handle real tasks such as answering client questions, supporting marketing conversations, and generating content that matches your brand voice.
The key difference between a generic chatbot and a useful agent is focus. A strong agent has a clear job, clear boundaries, and clear sources of truth.
There are a lot of meanings to an AI Agent that you can learn about by reading our latest post on What Are AI Agents? The Complete 2026 AI Agents Guide.
The 3 Step No Code Process to Build an AI Agent
Most no code AI agents follow the same loop, regardless of platform. On Agent.so, that loop maps cleanly to crafting, training, and deploying.
Craft the agent: Define who the agent is, what it does, and how it should respond. This includes the role, audience, tone, and rules.
Train the agent: Add your resources so responses stay aligned with your business. Training is where your agent stops sounding generic and starts sounding like your brand, especially for high intent questions like pricing, policies, and service details.
Deploy the agent as an AI Widget: Turn the agent into an embeddable experience for websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. Widgets help you meet users where they already are, instead of forcing them into a separate tool.
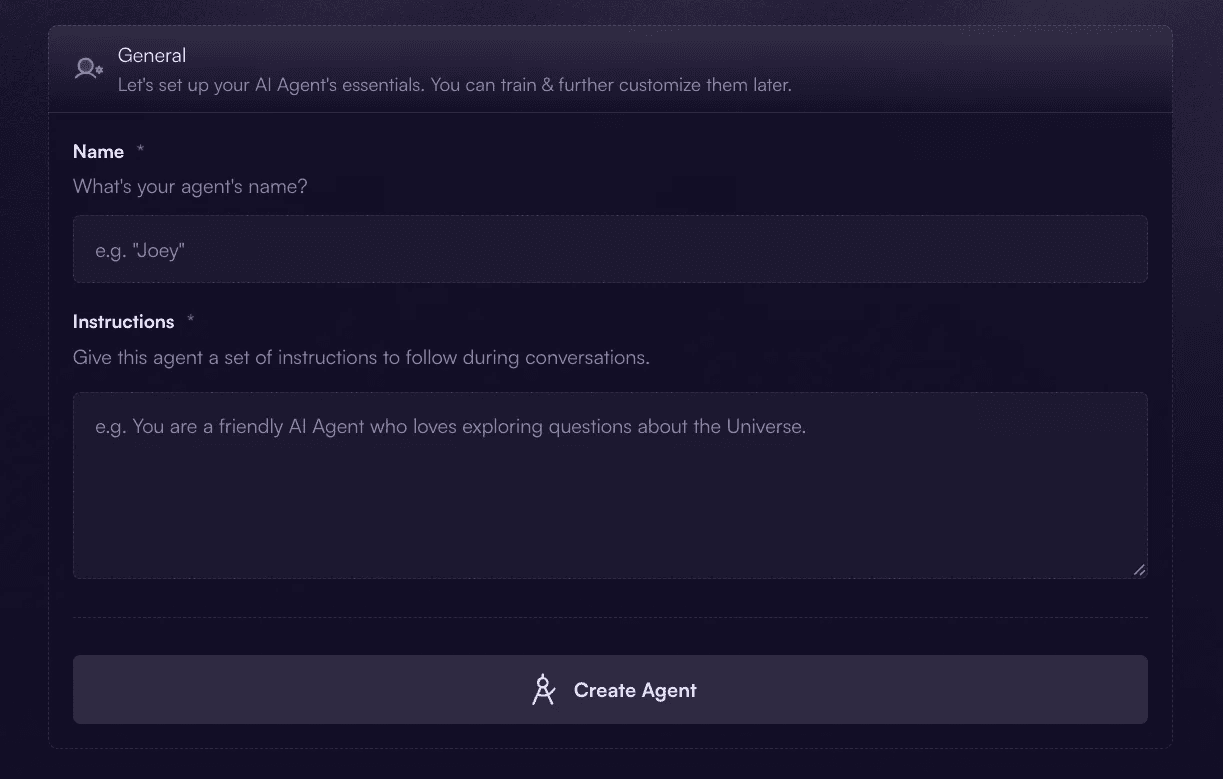
Step 1: Craft Your AI Agent with Clear Instructions
Crafting is where you set the foundation. Your goal is to make the agent predictable and helpful, not “smart sounding.”
Start by deciding what success looks like. Good agent scopes are narrow and measurable, such as product support for a specific feature, lead qualification for a single service, or onboarding guidance for a defined audience.
Then write instructions that remove ambiguity. If you want fewer hallucinations and more useful conversations, your instructions should answer these questions: What is the agent’s job? Who is it helping? What tone should it use? What should it never do? What should it do when it is unsure?
Treat this like a mini operating manual. The clearer the rules, the more consistent the agent feels.
Step 2: Train Your AI Agent on Your Resources
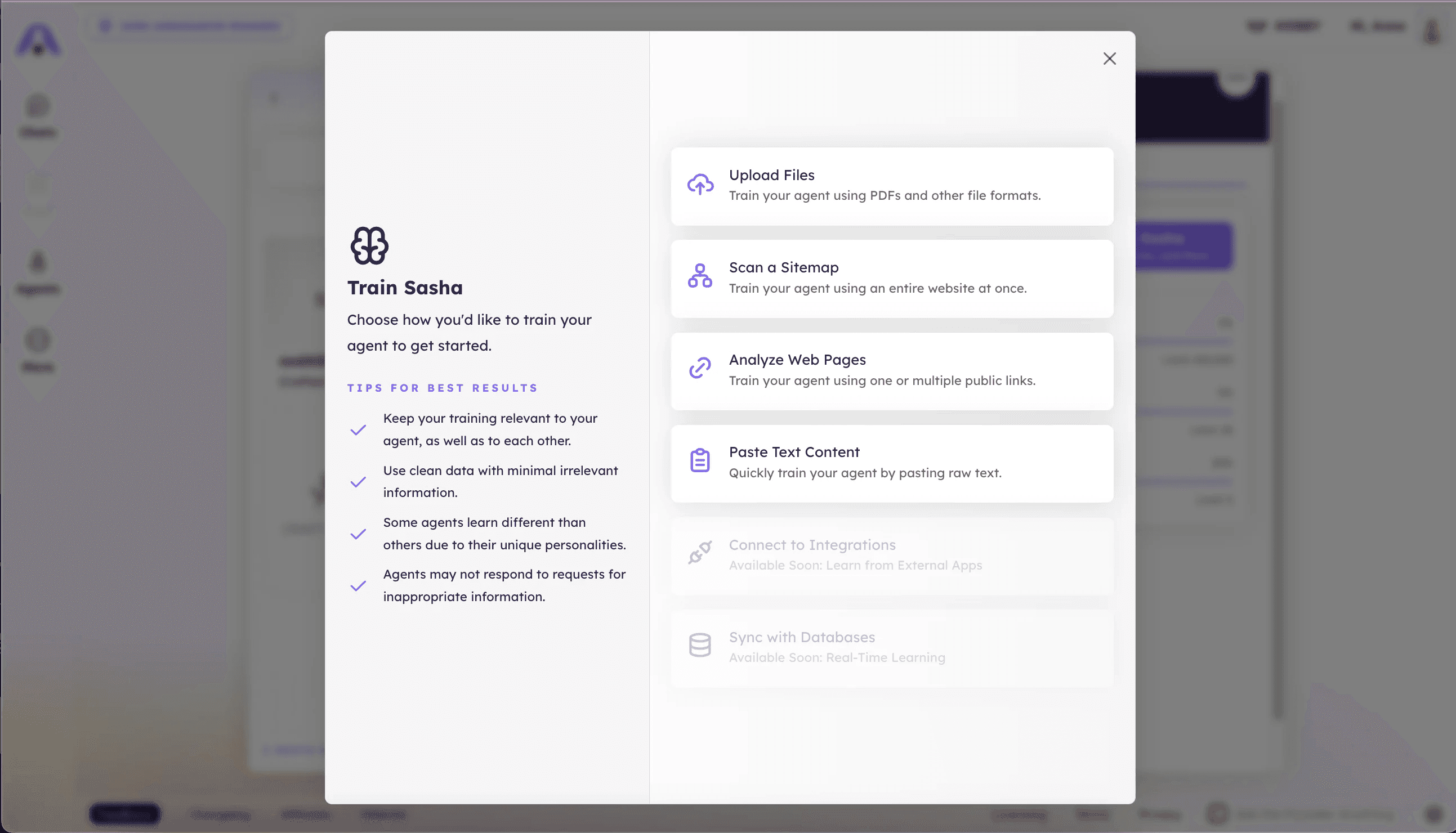
Training is what turns your agent from helpful to business ready. Instead of relying only on general knowledge, you connect the agent to the information you want it to reference and follow.
The best training sources are practical and specific, like FAQs and support documentation, pricing pages and service packages, policies and terms, product specs and internal playbooks, and brand guidelines with approved language.
When training is done well, the agent becomes faster and more confident for the questions that matter most. It can answer accurately, stay on brand, and handle repetitive inquiries without drifting.
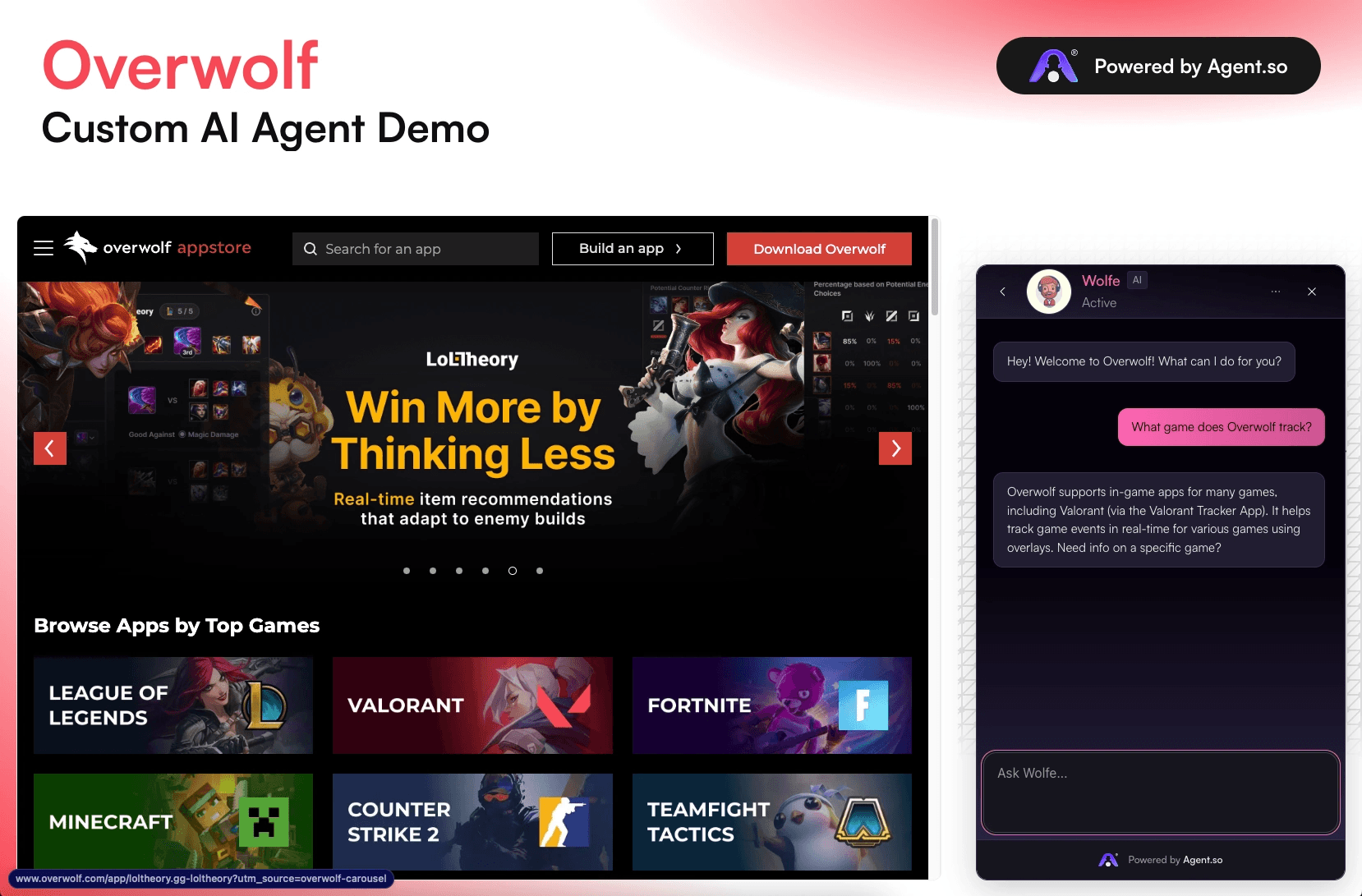
Step 3: Deploy Your AI Agent with AI Widgets
After crafting and training, the biggest mistake is keeping the agent hidden. Deployment is how you turn the work into outcomes.
Agent.so supports AI Widgets that you can embed into websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. That means your agent can support users directly on key pages like the homepage, pricing pages, service landing pages, product documentation, checkout flows, and support centers.
Widgets also create a tighter feedback loop. You get real questions from real users, which tells you exactly what to improve in instructions and training.
How to Make Your AI Agent Feel Smart On Day One
You do not need complex prompt engineering to get strong results. You need clarity and a practical rollout.
Write instructions like a job description. Include role, tone, boundaries, and what to do when unsure.
Train on the content you want it to follow. If it should quote a policy, include that policy.
Plan a handoff moment. Decide when it should recommend contacting a human, booking a call, or submitting a form.
Keep version one narrow. One audience, one problem, one success metric.
Deploy where questions already happen. Widgets are most effective when placed where users naturally hesitate or ask for help.
Common AI Widget Use Cases that Convert
If you are wondering what to build first, widgets are a great starting point because they put your agent in front of real users quickly. Agent.so highlights widgets for scenarios like client support, outreach style interactions, and marketing campaign conversations.
A strong first widget is a help desk assistant trained on your FAQ and policies. Once that works, the next step is a lead capture widget that qualifies inquiries, answers common objections, and routes people to the right offer.
Launch Your AI Agent on Agent.so
If you want to build and launch a no code AI agent without stitching together multiple tools, start on Agent.so. Craft your agent with clear instructions, train it on your resources, then deploy it as an AI Widget where your customers already are.
Sign up, craft and launch your first agent in minutes, then use the real questions people ask through your widget to refine its instructions and training data.
As your agent learns from better sources and clearer rules, it becomes more accurate, more on brand, and more helpful with every iteration, turning everyday conversations into a scalable support and lead generation channel.
Building an AI agent used to mean hiring engineers, stitching APIs together, and maintaining a messy stack of tools. In 2026, it can be much simpler. You create a role based assistant, teach it your content, then deploy it where people already interact with your brand.
This guide focuses on a practical, no code workflow using Agent.so. It is built around one idea: your agent should feel like a specialist, speak in your tone, and live in the channels that matter.
What an “AI Agent” Means Here
Here, an “AI agent” is a chat based assistant that behaves consistently like a specialist. You configure it with instructions and knowledge so it can handle real tasks such as answering client questions, supporting marketing conversations, and generating content that matches your brand voice.
The key difference between a generic chatbot and a useful agent is focus. A strong agent has a clear job, clear boundaries, and clear sources of truth.
There are a lot of meanings to an AI Agent that you can learn about by reading our latest post on What Are AI Agents? The Complete 2026 AI Agents Guide.
The 3 Step No Code Process to Build an AI Agent
Most no code AI agents follow the same loop, regardless of platform. On Agent.so, that loop maps cleanly to crafting, training, and deploying.
Craft the agent: Define who the agent is, what it does, and how it should respond. This includes the role, audience, tone, and rules.
Train the agent: Add your resources so responses stay aligned with your business. Training is where your agent stops sounding generic and starts sounding like your brand, especially for high intent questions like pricing, policies, and service details.
Deploy the agent as an AI Widget: Turn the agent into an embeddable experience for websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. Widgets help you meet users where they already are, instead of forcing them into a separate tool.
Step 1: Craft Your AI Agent with Clear Instructions
Crafting is where you set the foundation. Your goal is to make the agent predictable and helpful, not “smart sounding.”
Start by deciding what success looks like. Good agent scopes are narrow and measurable, such as product support for a specific feature, lead qualification for a single service, or onboarding guidance for a defined audience.
Then write instructions that remove ambiguity. If you want fewer hallucinations and more useful conversations, your instructions should answer these questions: What is the agent’s job? Who is it helping? What tone should it use? What should it never do? What should it do when it is unsure?
Treat this like a mini operating manual. The clearer the rules, the more consistent the agent feels.

Step 2: Train Your AI Agent on Your Resources
Training is what turns your agent from helpful to business ready. Instead of relying only on general knowledge, you connect the agent to the information you want it to reference and follow.
The best training sources are practical and specific, like FAQs and support documentation, pricing pages and service packages, policies and terms, product specs and internal playbooks, and brand guidelines with approved language.
When training is done well, the agent becomes faster and more confident for the questions that matter most. It can answer accurately, stay on brand, and handle repetitive inquiries without drifting.

Step 3: Deploy Your AI Agent with AI Widgets
After crafting and training, the biggest mistake is keeping the agent hidden. Deployment is how you turn the work into outcomes.
Agent.so supports AI Widgets that you can embed into websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. That means your agent can support users directly on key pages like the homepage, pricing pages, service landing pages, product documentation, checkout flows, and support centers.
Widgets also create a tighter feedback loop. You get real questions from real users, which tells you exactly what to improve in instructions and training.

How to Make Your AI Agent Feel Smart On Day One
You do not need complex prompt engineering to get strong results. You need clarity and a practical rollout.
Write instructions like a job description. Include role, tone, boundaries, and what to do when unsure.
Train on the content you want it to follow. If it should quote a policy, include that policy.
Plan a handoff moment. Decide when it should recommend contacting a human, booking a call, or submitting a form.
Keep version one narrow. One audience, one problem, one success metric.
Deploy where questions already happen. Widgets are most effective when placed where users naturally hesitate or ask for help.
Common AI Widget Use Cases that Convert
If you are wondering what to build first, widgets are a great starting point because they put your agent in front of real users quickly. Agent.so highlights widgets for scenarios like client support, outreach style interactions, and marketing campaign conversations.
A strong first widget is a help desk assistant trained on your FAQ and policies. Once that works, the next step is a lead capture widget that qualifies inquiries, answers common objections, and routes people to the right offer.
Launch Your AI Agent on Agent.so
If you want to build and launch a no code AI agent without stitching together multiple tools, start on Agent.so. Craft your agent with clear instructions, train it on your resources, then deploy it as an AI Widget where your customers already are.
Sign up, craft and launch your first agent in minutes, then use the real questions people ask through your widget to refine its instructions and training data.
As your agent learns from better sources and clearer rules, it becomes more accurate, more on brand, and more helpful with every iteration, turning everyday conversations into a scalable support and lead generation channel.
Building an AI agent used to mean hiring engineers, stitching APIs together, and maintaining a messy stack of tools. In 2026, it can be much simpler. You create a role based assistant, teach it your content, then deploy it where people already interact with your brand.
This guide focuses on a practical, no code workflow using Agent.so. It is built around one idea: your agent should feel like a specialist, speak in your tone, and live in the channels that matter.
What an “AI Agent” Means Here
Here, an “AI agent” is a chat based assistant that behaves consistently like a specialist. You configure it with instructions and knowledge so it can handle real tasks such as answering client questions, supporting marketing conversations, and generating content that matches your brand voice.
The key difference between a generic chatbot and a useful agent is focus. A strong agent has a clear job, clear boundaries, and clear sources of truth.
There are a lot of meanings to an AI Agent that you can learn about by reading our latest post on What Are AI Agents? The Complete 2026 AI Agents Guide.
The 3 Step No Code Process to Build an AI Agent
Most no code AI agents follow the same loop, regardless of platform. On Agent.so, that loop maps cleanly to crafting, training, and deploying.
Craft the agent: Define who the agent is, what it does, and how it should respond. This includes the role, audience, tone, and rules.
Train the agent: Add your resources so responses stay aligned with your business. Training is where your agent stops sounding generic and starts sounding like your brand, especially for high intent questions like pricing, policies, and service details.
Deploy the agent as an AI Widget: Turn the agent into an embeddable experience for websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. Widgets help you meet users where they already are, instead of forcing them into a separate tool.
Step 1: Craft Your AI Agent with Clear Instructions
Crafting is where you set the foundation. Your goal is to make the agent predictable and helpful, not “smart sounding.”
Start by deciding what success looks like. Good agent scopes are narrow and measurable, such as product support for a specific feature, lead qualification for a single service, or onboarding guidance for a defined audience.
Then write instructions that remove ambiguity. If you want fewer hallucinations and more useful conversations, your instructions should answer these questions: What is the agent’s job? Who is it helping? What tone should it use? What should it never do? What should it do when it is unsure?
Treat this like a mini operating manual. The clearer the rules, the more consistent the agent feels.

Step 2: Train Your AI Agent on Your Resources
Training is what turns your agent from helpful to business ready. Instead of relying only on general knowledge, you connect the agent to the information you want it to reference and follow.
The best training sources are practical and specific, like FAQs and support documentation, pricing pages and service packages, policies and terms, product specs and internal playbooks, and brand guidelines with approved language.
When training is done well, the agent becomes faster and more confident for the questions that matter most. It can answer accurately, stay on brand, and handle repetitive inquiries without drifting.

Step 3: Deploy Your AI Agent with AI Widgets
After crafting and training, the biggest mistake is keeping the agent hidden. Deployment is how you turn the work into outcomes.
Agent.so supports AI Widgets that you can embed into websites, apps, messaging platforms, and other digital environments. That means your agent can support users directly on key pages like the homepage, pricing pages, service landing pages, product documentation, checkout flows, and support centers.
Widgets also create a tighter feedback loop. You get real questions from real users, which tells you exactly what to improve in instructions and training.

How to Make Your AI Agent Feel Smart On Day One
You do not need complex prompt engineering to get strong results. You need clarity and a practical rollout.
Write instructions like a job description. Include role, tone, boundaries, and what to do when unsure.
Train on the content you want it to follow. If it should quote a policy, include that policy.
Plan a handoff moment. Decide when it should recommend contacting a human, booking a call, or submitting a form.
Keep version one narrow. One audience, one problem, one success metric.
Deploy where questions already happen. Widgets are most effective when placed where users naturally hesitate or ask for help.
Common AI Widget Use Cases that Convert
If you are wondering what to build first, widgets are a great starting point because they put your agent in front of real users quickly. Agent.so highlights widgets for scenarios like client support, outreach style interactions, and marketing campaign conversations.
A strong first widget is a help desk assistant trained on your FAQ and policies. Once that works, the next step is a lead capture widget that qualifies inquiries, answers common objections, and routes people to the right offer.
Launch Your AI Agent on Agent.so
If you want to build and launch a no code AI agent without stitching together multiple tools, start on Agent.so. Craft your agent with clear instructions, train it on your resources, then deploy it as an AI Widget where your customers already are.
Sign up, craft and launch your first agent in minutes, then use the real questions people ask through your widget to refine its instructions and training data.
As your agent learns from better sources and clearer rules, it becomes more accurate, more on brand, and more helpful with every iteration, turning everyday conversations into a scalable support and lead generation channel.
Guide
How To Build An AI Agent (No Code Guide)
Guide
How To Build An AI Agent (No Code Guide)



















